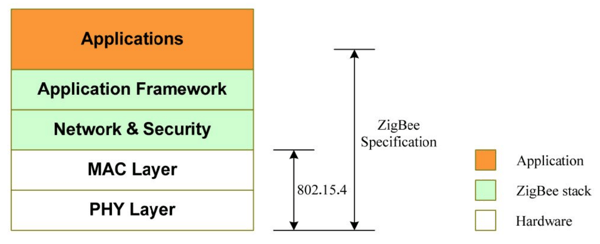
The ZigBee Protocol

It includes hardware and software standard design for WSN (Wireless sensor network) requiring high reliability, low cost, low power, scalability and low data rate. ZigBee-style self-organizing ad-hoc digital radio networks were conceived in the 1990s, but the IEEE 802.15.4-2003/ZigBee specification was ratified on December 14, 2004. And only half year later the ZigBee Alliance announces availability of Specification 1.0 (on June 13, 2005).
A WSN consist in inexpensive wireless sensor which are capable of collecting, storing, processing environmental information, and communicating to neighbors nodes. For example, a WSN, at home can be used for light control, heating ventilation air conditioning (HVAC), security monitoring, and emergency event detection. And for industrial control can be used to improve the current manufacturing control system, detect unstable situations, control production pipelines, and so on.
ZigBee provides ultra low consumption and efficiency (thanks to the adaptable duty cycle, the low rate rates and the low coverage radio), and enable large scale networks for the WPN, making it one of the most convenient standards for this purpose. 
The ZigBee Alliance
The ZigBee alliance objective is to work on the interoperability issues of IEEE 802.15.4/ZigBee protocol stacks. There are three levels of membership: Adopter, Participant, and Promoter.
- Adopter: Offers access to final, approved specifications, use of the Zigbee Member logo, participation in interoperability events, workshops and developers conferences.
- Participant: Offers full participation in all Alliance committees, work/task groups and member meetings. Participants earn voting rights in work groups and have early access to all Zigbee Alliance standards and specifications in development.
- Promoter: Offers automatic voting rights in all work groups, final approval rights on all standards and a seat on the Alliance Board of Directors
The IEEE 802.15.4
Before start being more technical about ZigBee, let’s introduce the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. Basically what It does is to specify the physical and data link layer protocols for low-rate wireless personal area network (LR-WPAN) and it was defined in 2003.
Devices in a LR-WPAN can be classified as full function device (FFDs) and reduce function devices (RFDs). One device is designated as the PAN coordinator which is the responsible for maintaining the network and managing other devices
It also defines two types of network topologies: star topology and peer-to-peer topology.
The star pattern is structured, where the coordinator of the network will necessarily be the central node. Peer-to-Peer networks can form arbitrary patterns of connection, and their extension is limited by the distance between each pair of nodes.
It can operate on channel 868 MHz in Europe, 916 MHz in America and Australia and 2400 MHz worldwide, also some other were added.
The Physical layer (PHY)
Is the layer that provides the data transmission capabilities. There are three different states defined for the devices: Transmitting, receiving and sleeping. This allows to the device to save energy when duty cycles are defined and the device sleeps. It also characterize the link quality/strength of a received signal of a link - Link Quality Indication (LQI).
The Data Link Layer
Is the layer in charge of data transference between the nodes of the network. It introduces - on the MAC sublayer - the superframe structure. The superframe is defined by the time between two beacons send by the coordinator of the network. The superframe can be divided between active period and inactive period, this - together with the sleeping state- allows to save energy during the inactive periods.
The beacons are used also to synchronizing with other devices, announcing the existence of a PAN, and informing pending data in coordinators.
ZigBee - First release
The ZigBee protocol uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for the first two layers and adds the network and security, and framework protocol on top of it.
The network layer provides reliable and secure transmission among devices.
It defines three types of devices:
- ZigBee Coordinator: responsible for initializing, maintaining and controlling the network. There is one and only one per network
- ZigBee Router: connected to the coordinator or other routers. It can have zero or more children nodes. Participate in multi hop routing
- ZigBee End Devices: does not participate in routing
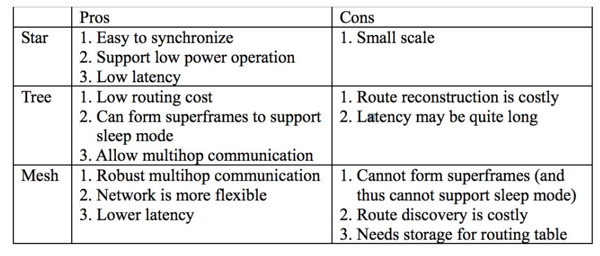
Also it defines three types of network topology: Star, tree and mesh.
In the star topology there is no presence of ZigBee Router. There is only a ZigBee Coordinator and zero or more ZigBee End Devices.
In the case of the tree, or cluster tree, topology the ZigBee Coordinator and also the ZigBee Router can announce beacons. The ZigBee Router can define dynamics duty cycle per cluster allowing devices to go to sleep not depending on the ZigBee Coordinator but on a more close ZigBee Router. The device would choose a slot and transmit its beacon to avoid collision. It also enables guaranty bandwidth (GTS).
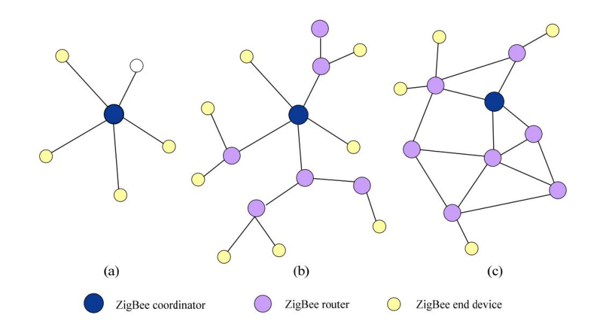
Finally in the mesh topology there is no synchronization, therefore no beacon enable mode, meaning that the ZigBee Coordinator and the ZigBee Routers must be always on. And because of the dynamics of the network there is no bandwidth guaranty.
ZigBee 3.0 - Last release
On the last ZigBee release there were several new features and improvements. Some of the most importants are:
Support of two kinds of security models, the Centralized Security Network and Distributed Security Network.
- In a Centralized Security Network only the ZigBee Coordinators or Trust Centers can start centralized networks, when a node joins it receives the network key and establish a unique TCLK.
- In a Distributed Security Network there is no Central Node or Trust Center, every router is able to start distributed networks by their own. When a node joins to the network it only receives the network key.
Incorporation of new specifications such as:
- ZigBee Pro 2015
- Base Device Behaviour
- Green Power Basic Proxy
- ZigBee Cluster Library (Rev. 6)
- ZigBee Application Architecture
- ZigBee Lighting & Occupancy Device
Advantages of IoT with ZigBee
There are several advantages of using the ZigBee protocol when comparing with other protocols for WSN.
- One of the main advantage is that ZigBee is standardized at all layers, this ensures that products from different manufacturers are compatible with each other.
- Other advantage is the power of the mesh, devices tend to connect with every near device, that makes every node of the network reachable from every other node and expanding the network geographically, also providing self healing, if the preferable path to a node fails there are other path to reach the node. The more devices you have the more reliable the network is.
- Low consumption of energy and working in the network even without the necessity of a battery (Green Power). Energy-harvesting devices lack batteries, getting it by extracting the energy they need from the environment (by tapping into motion, light, piezo/pressure, or the Peltier effect). This is especially effective for devices that are only sometimes on the network (when they have power) and lets these devices securely go on and off the network, so they can be off most of the time and not need any energy.
- And high scalability, ZigBee networks can to thousand of devices and they will communicate with each other using the best available path.
Some IoT applications using ZigBee
- Smart Parking Lot
- An Intelligent Transportation Systems Architecture using Wireless Sensor Networks
- Zigbee standard implementation for a wireless temperature system
Other protocols to look at:
- 6lowpan
- WirelessHart
- ISA100
Sources:
ZigBee Wireless Sensor Networks and Their Applications, Meng-Shiuan Pan and Yu-Chee TsengEngineering IEEE 802.15.4/ZigBee Wireless Sensor networks. Anis Koubaa
ZigBee 3.0 – The Open, Global Standard for the Internet of Things
What’s the Difference between ZigBee RF4CE and ZigBee Green Power? - Stephen Mraz


