Cloud Computing Scalability: What Is It and Why It’s Important?

Contents
Technology can make or break a business. Choosing the right technology is therefore crucial.
With more businesses migrating to cloud computing, scalability within that architecture is key. This article looks into what cloud computing scalability is and why it’s important for your company.
First, let’s do a quick cloud computing recap.
What are the characteristics of cloud computing?
Cloud computing delivers on-demand services and resources to businesses. These include data storage and processing power. They’re delivered over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The ten major characteristics of cloud computing are:
- Scalability
- Security
- Economical
- Automation
- Self-service and on-demand
- Easy to maintain
- Pooling of resources
- Reporting service
- Availability and resilience
- Considerable network access
Cisco estimates cloud data centers will process 94% of workloads in 2021. Considering these positive characteristics, it’s no wonder cloud computing is here to stay.
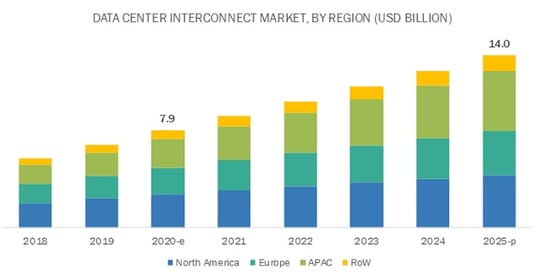
Source: MarketsAndMarkets
What are the basic clouds in cloud computing?
There are four main cloud environments in cloud computing:
- Public cloud. Offered by third-parties, anyone can use a public cloud.
- Private cloud. Not publicly available, one entity alone uses a private cloud.
- Hybrid cloud. A model that blends a public cloud and a private cloud.
- Multi-cloud. A structure combining services from more than one cloud vendor.
These cloud models offer three main types of service:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). The most flexible type of cloud service, offering a completely virtualized computing infrastructure. An example is Microsoft Azure.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). A bit less specialized, but more than pure infrastructure. Heroku is a PaaS example.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). A fully developed software solution that’s available on a subscription basis. Google Apps is an example of SaaS.
Now we’ve refreshed on the basics, let’s move on to a cloud scalability definition.
What are scalability and elasticity in cloud computing?
These two terms are often used interchangeable, but they’re not the same thing.
Scalability
Cloud scalability is all about adding or reducing IT resources to meet changes in demand. It’s the ability of a system to accommodate larger or smaller loads.
Businesses can scale up or down (vertically) and out or in (horizontally). For example, scaling up makes hardware stronger; scaling out adds additional nodes. More on these later.
If your business requires more data storage capacity or processing power, you want a system that can scale easily and quickly.
Cloud computing solutions can do just that, contributing to why the market has grown so much in recent years. By using existing cloud infrastructure, third-party cloud vendors can scale with minimal disruption.
A scalability in cloud computing example? We helped healthcare startup Nodus Medical scale their medical platform in a secure and robust way. Mitigating to the cloud facilitated their ability to scale.
By contrast, let’s consider a company with on-premises physical infrastructure. A business like that will find scaling time-consuming and expensive.
Elasticity
Elasticity is all about the actual increasing or decreasing of resources. It's the ability to fit resources to cope with loads dynamically – usually in relation to scaling out. For example, when a load increases, the system scales by adding more resources. When demand drops, shrink and remove resources.
Elasticity is most important in pay-per-use cloud environments where you don't want to pay for resources you don't currently need, but want to meet rising demand when required.
Scalability is a property of a system to handle a growing amount of work by adding resources to the system – the availability to do the change. Elasticity is the carrying out of the change in resources.
Scalability is a part of solution design; elasticity is an action.
We’ve established the difference between cloud elasticity and cloud scalability. Now, let’s dig into what cloud scalability does for your business.
Advantages of cloud scalability
Cloud computing scalability benefits drive cloud adoption. The reasons businesses use the cloud to scale include:
Cost-efficient
With zero upfront costs on costly equipment, scaling via the cloud saves your business money. With none of these initial outlays, there won’t be expensive upgrades either. There are savings in terms of IT staff, power, and cooling, too.
Waste and risk both minimize because you only pay cloud providers for what you use. What’s more, many applications run more cost-effectively in the cloud.
Convenienct
Gone are the days of setting up physical hardware. Instead, IT employees can easily add additional virtual machines, often at the click of a button or two. That saves time, leaving them free to work on revenue-generating projects.
Fast and flexible
The beauty of cloud scalability is you can respond and adapt to shifting business requirements with speed and efficiency. For example, you can update storage and systems as and when you need to. As your business faces new challenges, cloud scalability offers you versatility and freedom.
You can reshape your infrastructure easily and even redesign your model. For instance, you can move from a private cloud model to a hybrid cloud or multi-cloud system if that suits your changing needs better.
Greater power
Whatever the size of your business, cloud computing offers access to high-powered resources. Small or large, cloud computing scalability allows access to powerful software and data tools. Historically, infrastructure limitations prevented organizations from scaling quickly. Buying equipment and implementing processes took time and money.
Disaster recovery
Scalable cloud applications allow you to reduce disaster recovery costs. How? You no longer have to foot the bill for the expensive building and maintenance costs associated with a secondary data center.
Storage
Scalable cloud storage is crucial for a company that’s growing. Businesses can use cloud computing to scale their data storage to fit their needs. That means physical infrastructure and the associated costs become a thing of the past.
When to use cloud scalability?
Scalable business models are nothing new: they allow businesses to meet changing needs. Cloud scalability applies to the IT side of your business. By making the most of cloud scalability, your business stays competitive.
Scalability drives migration to the cloud. When a business grows and needs more resources, cloud scalability enables a rapid response. It also offers a cost-effective solution.
How to achieve cloud scalability?
Virtualization is what makes cloud scalability possible.
There are limits to the resources and performance of physical machines. On the flip side, virtual machines are flexible and easily scaled. It’s possible to move virtual machines to a different server or host them on multiple servers. Upgrades to larger virtual machines are possible, too.
What’s more, with technological advances such as better internet speeds and 5G, virtual machines are more productive than ever.
How your business achieves scalability depends on your cloud model. For example, third-party public cloud vendors have access to significant amounts of resources. That allows for speedy and cost-friendly scaling. Equally, private clouds and hybrid clouds offer customized, scalable solutions.
There are usually two ways to scale a cloud-based solution:
- Contact your cloud provider and request it.
- Add the required resources yourself via an online portal.
Some solutions can be auto-scaled. That means setting them to scale up or down based on the conditions you input. For example, you may set a rule to automatically scale up when you’re running out of storage space. Cloud solutions such as Kubernetes and Google Cloud Platform (GCO) offer that.
Scalability
Cloud scalability is dynamic and easy to achieve. Having said that, there are questions to ask yourself. For example, is scaling in or out the best option for your business needs? That may change over time. There are best practices to keep in mind to maximize cloud scalability, such as:
Ongoing testing
To reach the best business decisions in terms of scaling, performance testing is vital. Your IT team must measure factors like CPU load, memory usage, and response time.
Auto-scaling
Think about automating processes to help optimize cloud scalability. As we mentioned above, it can be beneficial to set rules to automatically scale when your business reaches certain thresholds. That way, performance isn’t impacted.
Key features of cloud scalability
Now you know how to achieve cloud scalability, what are the main features of cloud scalability? These include the following:
- Sizeable difference. Scaling involves a significant change. It doesn’t mean a minor alteration.
- Grow or shrink. When a business scales, it changes in size. That can mean increasing or decreasing.
- Speed. Scaling via the cloud is quick. It’s certainly faster than buying and setting up physical hardware yourself.
- Ease. It’s relatively easy to scale using a cloud solution. Without virtualization, scaling would be expensive, via physical machines.
- Not disruptive. To scale doesn’t mean to replace. You’re adding or removing resources, meaning there should be minimal downtime. For example, let’s say you own an online store, and the summer sales are coming. You can set up an auto-scale rule with Microsoft Azure to increase virtual machines when traffic hits a certain amount. That way, you can scale up to handle the additional load. By contrast, switching from Google Apps to Microsoft Office 365 is replacing, not scaling.
Types of cloud scalability
It’s important to configure your cloud environment to best suit your needs. There are various types of scalability available to businesses, solving different scalability issues. These include:
Vertical scaling
Vertical scaling is also known as scaling up (or down). It means resizing an existing resource with no change to your code. You’re simply running the same code on a higher- or lower-spec machine.
When you scale vertically, you enlarge or diminish a resource to change the capacity of your existing infrastructure. That infrastructure becomes more or less powerful.
For example, you could move a web application to a larger virtual machine or add more CPU to an existing server.
Horizontal scaling
Horizontal scaling also goes by the name scaling out (or in). When your business scales horizontally, you add or remove instances of a resource or infrastructure. It involves breaking a sequential piece of logic into smaller pieces. That’s then executed in parallel across multiple resources or infrastructures.
With Amazon Web Services (AWS), an example of horizontal scaling is changing the number of nodes in a computing system. The size of each individual node remains the same.
Horizontal scaling is more labor-intensive than vertical scaling. It’s particularly important for organizations with high availability services requiring minimal downtime.
High availability (HA)
The aim of a high availability system is being available 99.999% of the time, or as close to that as possible. Usually, that means configuring a failover system with the ability to handle the same workloads as the primary system.
Fault tolerant (FT)
A fault tolerant system is similar to a high availability system, but goes a step further by guaranteeing zero downtime.
Disaster recovery (DR)
If you have systems configured with HA or FT, do you need DR? DR goes beyond HA and FT, consisting of a complete plan to recover critical business systems and normal operations if a catastrophic natural disaster or major weather event occurs.
How do these relate to scaling? When a system scales, it can handle an increase in demand without any impact on performance or availability.
Diagonal scaling
Diagonal scaling refers to a combination of vertical and horizontal scaling. Your business grows vertically within existing infrastructure until it reaches a tipping point. At that stage, you add more resources to scale out horizontally.
Conclusion: What is cloud scalability and why is it important?
Cloud scalability refers to increasing or decreasing resources to meet changes in demand. A scalable cloud architecture is key to business growth and helps you stay competitive. Virtualization makes cloud scalability possible. Though how a business achieves scalability depends on your cloud model.
Businesses are migrating to the cloud to harness scalability opportunities. Why? Scaling cloud services comes with many advantages. For example, the benefits of cloud scaling range from cost savings to flexibility.
Having said that, it’s important to think about how your business should scale, to get the optimal experience. Is horizontal scaling optimal for you? Or should you scale vertically? Is auto-scaling right for your organization? Whatever the answers, cloud computing scalability is important for your company. For more useful information on cloud computing scalability, head to our cloud technology section.
