What Is a Blockchain and How Does It Work?

However, many people still don’t understand what blockchain technologies are and think that it’s only related to cryptocurrencies.
In this article, we’ll try to explain the idea of how blockchain works from a technical perspective. We will also talk about the benefits and opportunities for businesses that a blockchain system can provide.
What is a blockchain in simple terms?
As the name suggests it’s a chain of data blocks where each of them contains information about the previous block and the next block, usually transaction records. These blocks are handled by nodes called miners using computing power. These groups of nodes create a connected graph called a network.
Each node receives a price for sharing power for a network as a unit of some digital currency (or virtual currencies), called cryptocurrency. This assigned digital asset depends on the type of blockchain protocol, for example, ethereum blockchain, bitcoin blockchain or other virtual currencies existing in the market.
When it comes to blockchain technology, the huge amount of knowledge is related to cryptography because data stored in multiple blocks is encrypted. The reason is that the blockchain network is accessible for everyone but in order to get a readable form, a private key to decrypt a message is required. The private key is like a password for block encryption.
What is the difference between a wallet and an account?
Users that want to have access to their digital currency need an account or a wallet. However, there are large differences between the two of them. First of all, wallets are created locally and only the user has access to it by keeping a private key that is the single way to get access to that account. If the private key is stolen, the funds also will be lost forever. It makes a more secure solution than accounts.
| Decentralized account | Decentralized wallet | |
| Target | Novice users | Experienced users |
| Private key | Secured by platform | Only users have access |
| Asset custody | Platform | Users |
| Security | High: Data is protected on a highly secure private chain | Very high: Impermeable to hacks if private key is stored safely by the user |
| Cenralized services |
Health Management Products Lending OTC Trading Exchange |
N/A |
| Transaction fees | Free for transfers between decentralized accounts | Mining fees for transfers |
| Transaction speed | Instant | Depends on mining fee and traffic |
The accounts have private keys that are stored by highly secure private chains. In case of hacker attack, private keys can be stolen and this causes a security issue. On the other hand, platforms that offer accounts provide a way to recover passwords which are connected with the account.
When it comes to blockchain transaction fees and how blockchain works, the cost of the financial transaction requires a mining fee and the transaction speed depends not only on it but also traffic in the network. Accounts have an instant transaction speed and transactions between decentralized accounts are free.
To sum up, accounts are for novice users and wallets are for experienced blockchain users because it requires broader knowledge about blockchain technology and a blockchain strategy.
What is a network node in blockchain?
The nodes share their hardware resources in order to maintain the graph called a network. The complexity of the network grows with the amount of nodes in the network. It means that the more nodes there are, the harder it is to maintain the network and the cost of every change is bigger.
The node receives funds that can be transferred into another wallet. Very often they are some pieces of cryptocurrencies and they are stored in the user's wallet.
There are three types networks:
- Centralized networks
- Decentralized networks
- Distributed networks
| Centralized | Decentralized | Distributed | |
| Network and resources | Maintained and overseen by single entity in centralized location | Network members own and share resources. Maintenance is a challenge as no one owns the resources. | Scattered in different data centers. Network provider owners it. |
| Components | Maintained and overseen by central entity | Each member has the same copy of distributed ledger | Maintained and overseen by solution provider |
| Data | Central entity maintain and overseen it | Only added through group consensus | Usually owned and managed by customer |
| Control | Central entity controls it | No one owns the data and everyone owns the data |
Usually, network provider, solution provider and customer share responsibility
|
| Single point of failure (SPOF) | Yes | No | No |
| Error tolerance | Low | Very high | High |
| Security | Maintained and overseen by central entity | Increases as x of network members increase | Typically, network provider, solution provider and customer share responsibility |
| Performance |
Maintained and overseen by central entity | Decreases as x of network members increase | Increases as network/hardware resources enlarge |
Source: AWS Amazon: What is Decentralization in Blockchain?
Decentralized networks are the most popular in blockchain systems because most technologies use them, however, blockchain applications don’t determine its type of network. They are based on decentralized nodes that can communicate with each other. The characteristic property of digital currency is that none of the nodes have ownership.
The other approach is on a centralized network. There is a single, main entity that maintains almost everything, for example, security, storing data, control and performance. The main disadvantage of a centralized network is susceptibility to a single point of failure.
The last type of network used in applications is a distributed network where responsibility is distributed across other entities like network providers, customers and solution providers.
Currently, the market offers hundreds of cryptocurrencies. Almost all of them are blockchain based and each of them works on a separate network. These networks are publicly available, which means everybody can connect to the network as a node and take part in mining.
On the other hand, for project purposes it’s possible to have private blockchain networks based on other public blockchain networks like ethereum or bitcoin blockchain. The authors of ethereum blockchain provide a client that allows creating a single node that is not connected to a global network, allowing users to create a private blockchain network.
For development purposes it’s worth investing time in creating a test private blockchain network. Due to the fees alongside activities such as bitcoin transactions, it saves money because every written operation into the blockchain network costs money.
In the case of test networks we pay virtual funds that exist only in private blockchain networks. Doing it this way, some kind of new cryptocurrency is created because it’s a fork of an existing public blockchain network into a private network.
Creating custom networks allows Web3.js library and Docker. You can create, for example, an ethereum network using docker-compose and ready Docker images from the public blockchain network.
Then operations on that digital currency network can be handled by features offered by Web3.js library. There is also a possibility to create a blockchain solution not only by yourself, but also using the cloud.
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a service that uses a decentralized blockchain network (Amazon Managed Blockchain). The service allows you to create and record transactions with 2 nodes without knowing each other.
Transactions and smart contracts
The core of the blockchain data is made up of transactions and smart contracts. They are an implementation of communication between nodes and operations on blockchain networks.
Transactions are operations between 2 wallets that transfer funds with some binary message and have a transaction fee. In the case of ethereum protocol it’s gas. The speed of when a transaction occurs mostly depends on traffic in the blockchain network.
When we talk about blockchain technology it’s hard not to mention smart contracts. They are functions that are deployed into the entire network and called from code level.
From a blockchain perspective it's an ordinary transaction with text message as a code converted into binary form. Smart contracts are mostly written in Solidity language and then compiled into binary form understandable by machine.
Business value of blockchain
Blockchain technology is an innovative step forwards in the future of finance, but let’s focus on the now and on the business aspect. When we talk about business value, the important aspects are metrics that we can measure if something is worth investing money, time or employees.
According to McKinsey, there are 3 metrics that indicates impact idea for business:
- Revenue creation - How blockchain technology will turn out into profits for an organization or company.
- Cost reduction - In every business there exist processes that can be reduced. This metric shows impact for reducing costs for some processes.
- Consumer impact - This is related to how blockchain adoption will have an impact for end users and provides overlooked needs.

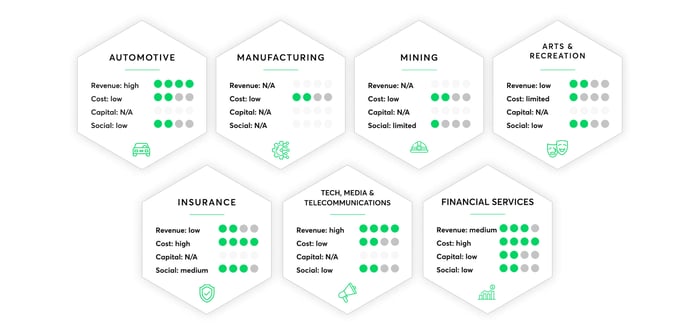
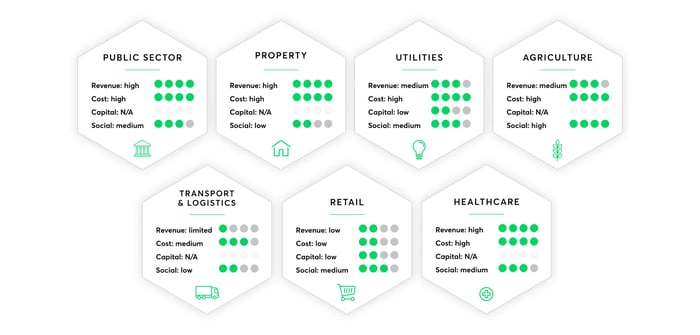
These 3 metrics can be taken into account while considering employing blockchain in a project or company. There are certain industries in which blockchain would be something innovative and will help grow faster than expected.
Blockchain in fintech
Anyone who uses the modern banking system can see how blockchain technology could improve the process. Currently, international transfer can take even longer than blockchain - up to a few days - and it costs extra money.
This is because central banks and currencies belong to centralized financial services or central authority. Blockchain eliminates this bottleneck and sends money ad hoc. However, this decentralization also means cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin are often used for money laundering.
It’s not only about sending money, but also verification to validate transactions and for recording transactions. The process of checking if the person is eligible for accpeting an application for a credit can take a few days or even weeks.
Extorting money is the problem that many financial services struggle with. The problem that decision makers have is the basic question whether the data from application for a credit are true. Blockchain networks are built as a structure of confirmations that can be used for recording transactions and verifying monetary transactions.
People involved in the process would be able to analyse more applications and clients would wait shorter for a decision than they would under a central authority. The blockchain revolutions makes the processes shorter with higher performance and bigger revenue.
Why do companies invest in blockchain?
As explained above, blockchain already brings value to industries such as fintech, healthcare, automotive , and insurance. Business invest in blockchain because of the advantages it can bring: decentralization, transparency and security, among others. Blockchain allows to enhance operations and payments options. Verification of various business processes can happen without third-party validation.







